Managing your finances has become easier than ever. Open Banking is leading the way by simplifying how individuals and businesses handle their money. This guide will walk you through what Open Banking is, how it works, the benefits it offers, potential risks, and its impact on the financial world.
At its core, Open Banking refers to a system that allows third-party financial service providers to access your financial information with your consent. This information includes your transaction history, account balances, and other relevant data. Open Banking relies on Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to facilitate the secure sharing of this information between banks and authorized third parties.
How Does Open Banking Work?
Open Banking operates on a simple yet powerful premise: it empowers you to share your financial data securely with third-party service providers. Here's how it works:
1. User Consent: You, as the account holder, grant explicit permission for a third party to access your financial data. This consent is typically given through a secure authentication process.
2. API Integration: Once you've given your consent, the third-party provider connects to your bank through APIs, which act as intermediaries to access your financial information.
3. Data Retrieval: The third-party provider retrieves the specific data it needs, such as your transaction history or account balance, depending on the service you've chosen.
4. Service Delivery: With the necessary data in hand, the third-party provider can offer various financial services, such as budgeting apps, investment advice, or loan applications.
What Kinds of Open Banking Services Are There?
Open Banking has paved the way for a wide range of innovative financial services and applications, including:
- Budgeting and Financial Management Apps: These apps help you track your spending, set savings goals, and make informed financial decisions.
- Payment Initiation Services: They allow you to initiate payments directly from your bank account without going through a traditional payment gateway.
- Account Aggregation Services: These services consolidate your financial information from multiple accounts and banks into one convenient dashboard.
- Personalized Financial Advice: Some platforms analyze your financial data to provide tailored advice on investments, insurance, and more.
- Access to Competitive Loan Offers: Open Banking enables you to share your financial information with lenders to receive personalized loan offers with favorable terms.
What Problem is Open Banking Solving?
Open Banking aims to address several key challenges in the financial industry:
- Limited Access: Traditional banks often restrict access to financial data, making it difficult for customers to switch banks or access innovative services.
- Fragmented Financial Management: Before Open Banking, it was challenging to consolidate and manage finances across multiple institutions.
- Lack of Personalization: Open Banking allows for more personalized financial services, tailored to individual needs and preferences.
- Innovation and Competition: It fosters competition and encourages the development of new financial products and services, benefiting consumers.
What Are the Risks of Open Banking?
While Open Banking offers numerous benefits, it's essential to be aware of potential risks:
- Data Security: The sharing of financial data introduces security concerns. It's crucial for banks and third-party providers to implement robust security measures to protect sensitive information.
- Fraud: Criminals may attempt to exploit vulnerabilities in the system to gain unauthorized access to financial data or engage in fraudulent activities.
- Privacy Concerns: Some individuals may be uncomfortable with the idea of sharing their financial data, even with their consent.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring that all parties involved comply with relevant regulations and standards is essential to mitigate risks.
Open Banking Security: How Safe Is Your Data?
Open Banking takes data security seriously. To safeguard your financial information, banks and third-party providers implement the following security measures:
- Strong Authentication: Secure authentication processes, such as two-factor authentication (2FA), are used to verify your identity.
- Encryption: Data transferred between parties is encrypted, making it difficult for unauthorized individuals to intercept and decipher.
- Authorization Controls: You have control over which third-party providers can access your data and for what purposes.
- Regulatory Oversight: Governments and regulatory bodies impose strict security and privacy standards on financial institutions and service providers.
How does Open Banking Impact the Market?
Open Banking has had a profound impact on the financial market. Here are some of the key effects:
- Increased Competition: Open Banking has lowered barriers to entry for new financial service providers, fostering competition that benefits consumers.
- Innovation: The industry has seen a surge in innovative solutions and apps that cater to specific financial needs and preferences.
- Improved Customer Experience: With more personalized services and easier access to financial information, customers now have a better experience.
- Efficiency: Streamlined processes and increased automation have made financial services more efficient and cost-effective.
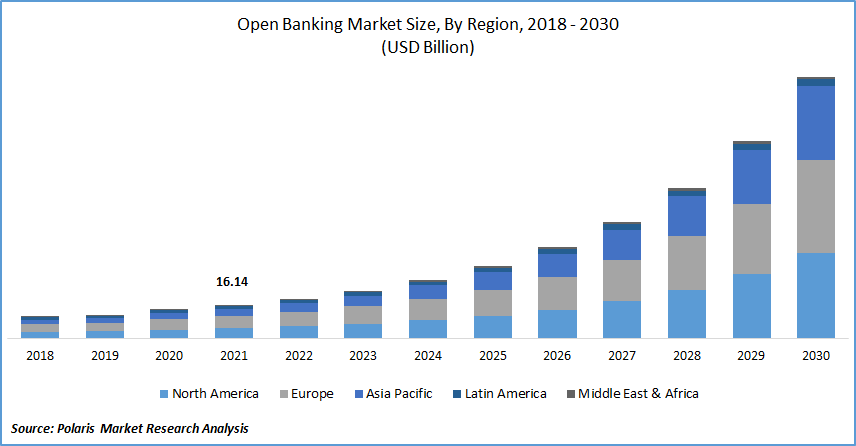
Open Banking Around the World
Open Banking is not limited to a specific region; it's a global phenomenon. Various countries have embraced Open Banking to varying degrees:
- Europe: The European Union has implemented the Revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2), which mandates Open Banking across EU member states.
- United Kingdom: The UK has been at the forefront of Open Banking, with the Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) mandating banks to open up their data to third parties.
- United States: While Open Banking in the US is not as regulated as in Europe, many financial institutions are adopting Open Banking principles to stay competitive.
- Asia: Countries like Singapore and Australia are also exploring Open Banking initiatives to drive innovation in their financial sectors.
FAQ's
- What is the essence of Open Banking?
Open Banking is a financial framework that allows individuals and businesses to share their financial data securely with third-party service providers. This data sharing is done with the account holder's explicit consent and aims to enable innovative financial services. - What is an example of Open Banking? An example of Open Banking is a budgeting app that accesses your bank account's transaction history and balance to provide you with insights into your spending habits and financial goals. This app can only access your data with your permission.
- What are the key principles of Open Banking? The key principles of Open Banking include user consent, secure data sharing through APIs, data protection, privacy controls, and regulatory compliance. These principles ensure that individuals have control over their financial data while maintaining security and privacy.
Open Banking is reshaping the financial services landscape by promoting innovation, competition, and improved customer experiences. While it offers tremendous benefits, it's crucial to be aware of the associated risks and the robust security measures in place to protect your data. As Open Banking continues to expand worldwide, it will undoubtedly play a significant role in shaping the future of finance. Embrace this exciting evolution, and make informed choices to enhance your financial well-being.