The world is no longer confined to traditional cash and card transactions. It has embraced a diverse array of payment options. This has now become a necessity. Payment methods are tailored to specific requirements. Among these, Alternative Payment Methods (APMs) and Local Payment Methods (LPMs) have emerged as significant players. It has changed financial interactions between businesses and consumers.
APMs and LPMs have often been used interchangeably. They both cater to distinct needs. APMs offer alternatives to conventional payment methods, broadening the financial landscape for consumers worldwide. LPMs, on the other hand, cater to the unique preferences and financial infrastructures of specific regions, ensuring seamless transactions even in areas with limited access to traditional banking. Here is a lowdown.
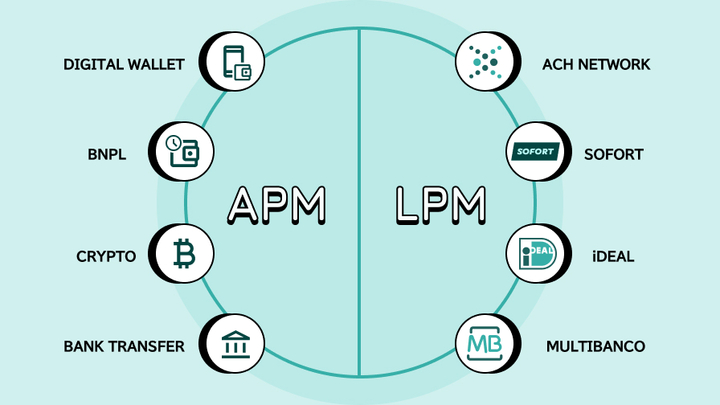
Understanding Alternative Payment Methods (APMs)
Alternative payment methods are at the centre of new-age digital transactions. They encompass a wide range of options, from digital wallets like Apple Pay and Google Pay to Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL).
APMs have gained immense popularity due to their convenience, speed, and security. They have empowered consumers to make purchases with a few clicks. This has bypassed the need for physical cards or cash. The rise of e-commerce has further fuelled the adoption of APMs.
APMs are convenient for consumers and beneficial for businesses. Businesses can also secure a bigger customer base when they offer APMs. This is true for those consumers who may not be able to avail traditional banking services.
APMs can also help reduce cart abandonment rates. Customers would be likely to complete a purchase if their preferred payment method is available. APMs have also become a crucial tool for businesses to improve their payment offerings and cater to evolving customer needs.
Understanding Local Payment Methods (LPMs)
Local payment methods are tailor-made for specific countries or regions. It works in regions where traditional banking penetration is low. LPMs take into account local preferences, financial regulations, and technological infrastructure.
LPMs can range from bank transfers and direct debit to mobile payments and cash-based vouchers. They have bridged the gap between the unbanked and the digital economy.
LPMs are more than just payment methods; they are cultural artefacts reflecting the unique financial landscape of each region. For instance, iDEAL, a popular LPM in the Netherlands, leverages the country's robust online banking infrastructure to enable secure and instant bank transfers. In contrast, OXXO, a Mexican convenience store chain, offers cash vouchers for online purchases, catering to the large unbanked population.
By embracing LPMs, businesses can tap into previously unexplored markets, encouraging financial inclusion and economic growth.
Geographic Impact on APM & LPM Strategy
The geographic location of both businesses and consumers plays a pivotal role in shaping their APM and LPM strategies.
A business operating in a developed country with a high rate of card penetration might prioritize digital wallets and BNPL services. A business expanding into emerging markets might need to consider mobile money or cash-based vouchers to cater to the local population's needs. Consumers in different regions have varying preferences for payment methods, often influenced by cultural norms, technological infrastructure, and financial regulations.
Understanding these geographic nuances is important for businesses looking to expand their reach and maximize their revenue potential. Tailored APM and LPM strategies to specific regions can create seamless payment experiences that resonate with local consumers. This can foster trust and loyalty. The influence of geography on APM and LPM strategies underscores the significance of adapting to local preferences in today's global business environment.
Leveraging Multiple Payment Gateways for APMs & LPMs
Incorporating multiple payment gateways is now a strategic necessity for businesses. It aims to thrive in the digital age. Businesses can offer a comprehensive suite of APMs and LPMs by partnering with various providers. This can help in catering to the diverse needs of their global customer base. This approach enhances customer experience and increases conversion rates. Customers, here, are more likely to complete a purchase if their preferred payment method is readily available.
Multiple payment gateways also offer redundancy and resilience. It ensures that transactions can still be processed even if one gateway experiences downtime. This is particularly important for businesses operating in regions with unreliable internet connectivity or those dealing with high transaction volumes.
By diversifying their payment infrastructure, businesses can mitigate risks and ensure seamless payment experiences for their customers. This is regardless of their location or preferred payment method. The ability to leverage multiple payment gateways is proof of the required adaptability and agility for success in the ever-evolving world of digital commerce.
Seamless APMs and LPMs Integration with Hyperswitch
Hyperswitch is a cutting-edge platform designed to simplify the integration of various payment methods, including APMs and LPMs. It provides businesses with a single API integration, eliminating the need for complex integrations with multiple payment providers. This streamlines the payment process, reduces operational overhead, and accelerates time-to-market for businesses seeking to expand their payment options.
Hyperswitch's intuitive interface and robust features empower businesses to manage their payment infrastructure efficiently. It offers real-time transaction monitoring, fraud detection, and customizable reporting, giving businesses complete control over their payment operations.
By leveraging Hyperswitch, businesses can utilize the complete potential of APMs and LPMs, expanding their reach, improving customer experience, and encouraging sustainable growth in the digital economy.